- South Africa
-
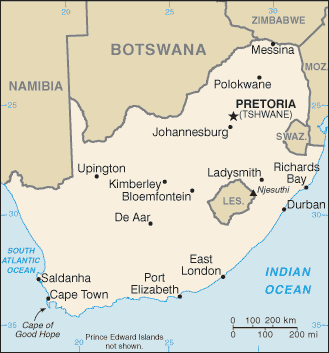 Introduction ::South AfricaBackground:Dutch traders landed at the southern tip of modern day South Africa in 1652 and established a stopover point on the spice route between the Netherlands and the Far East, founding the city of Cape Town. After the British seized the Cape of Good Hope area in 1806, many of the Dutch settlers (the Boers) trekked north to found their own republics. The discovery of diamonds (1867) and gold (1886) spurred wealth and immigration and intensified the subjugation of the native inhabitants. The Boers resisted British encroachments but were defeated in the Boer War (1899-1902); however, the British and the Afrikaners, as the Boers became known, ruled together beginning in 1910 under the Union of South Africa, which became a republic in 1961 after a whites-only referendum. In 1948, the National Party was voted into power and instituted a policy of apartheid - the separate development of the races - which favored the white minority at the expense of the black majority. The African National Congress (ANC) led the opposition to apartheid and many top ANC leaders, such as Nelson MANDELA, spent decades in South Africa's prisons. Internal protests and insurgency, as well as boycotts by some Western nations and institutions, led to the regime's eventual willingness to negotiate a peaceful transition to majority rule. The first multi-racial elections in 1994 brought an end to apartheid and ushered in majority rule under an ANC-led government. South Africa since then has struggled to address apartheid-era imbalances in decent housing, education, and health care. ANC infighting, which has grown in recent years, came to a head in September 2008 when President Thabo MBEKI resigned, and Kgalema MOTLANTHE, the party's General-Secretary, succeeded him as interim president. Jacob ZUMA became president after the ANC won general elections in April 2009.Geography ::South AfricaLocation:Southern Africa, at the southern tip of the continent of AfricaGeographic coordinates:29 00 S, 24 00 EArea:total: 1,219,090 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 25land: 1,214,470 sq kmwater: 4,620 sq kmnote: includes Prince Edward Islands (Marion Island and Prince Edward Island)Area - comparative:slightly less than twice the size of TexasLand boundaries:total: 4,862 kmborder countries: Botswana 1,840 km, Lesotho 909 km, Mozambique 491 km, Namibia 967 km, Swaziland 430 km, Zimbabwe 225 kmCoastline:2,798 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontinental shelf: 200 nm or to edge of the continental marginClimate:mostly semiarid; subtropical along east coast; sunny days, cool nightsTerrain:vast interior plateau rimmed by rugged hills and narrow coastal plainElevation extremes:lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 mhighest point: Njesuthi 3,408 mNatural resources:gold, chromium, antimony, coal, iron ore, manganese, nickel, phosphates, tin, rare earth elements, uranium, gem diamonds, platinum, copper, vanadium, salt, natural gasLand use:arable land: 9.87%permanent crops: 0.34%other: 89.79% (2011)Irrigated land:16,700 sq km (2012)Total renewable water resources:51.4 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 12.5 cu km/yr (36%/7%/57%)per capita: 271.7 cu m/yr (2005)Natural hazards:prolonged droughtsvolcanism: the volcano forming Marion Island in the Prince Edward Islands, which last erupted in 2004, is South Africa's only active volcanoEnvironment - current issues:lack of important arterial rivers or lakes requires extensive water conservation and control measures; growth in water usage outpacing supply; pollution of rivers from agricultural runoff and urban discharge; air pollution resulting in acid rain; soil erosion; desertificationEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:South Africa completely surrounds Lesotho and almost completely surrounds SwazilandPeople and Society ::South AfricaNationality:noun: South African(s)adjective: South AfricanEthnic groups:black African 79%, white 9.6%, colored 8.9%, Indian/Asian 2.5% (2001 census)Languages:IsiZulu (official) 23.82%, IsiXhosa (official) 17.64%, Afrikaans (official) 13.35%, Sepedi (offcial) 9.39%, English (official) 8.2%, Setswana (official) 8.2%, Sesotho (official) 7.93%, Xitsonga (official) 4.44%, siSwati (official) 2.66%, Tshivenda (official) 2.28%, isiNdebele (official) 1.59%, other 0.5% (2001 census)Religions:Protestant 36.6% (Zionist Christian 11.1%, Pentecostal/Charismatic 8.2%, Methodist 6.8%, Dutch Reformed 6.7%, Anglican 3.8%), Catholic 7.1%, Muslim 1.5%, other Christian 36%, other 2.3%, unspecified 1.4%, none 15.1% (2001 census)Population:48,601,098 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 26note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expectedAge structure:0-14 years: 28.3% (male 6,909,066/female 6,866,163)15-24 years: 20.6% (male 5,041,412/female 4,960,190)25-54 years: 38.1% (male 9,561,452/female 8,948,398)55-64 years: 6.9% (male 1,450,420/female 1,916,960)65 years and over: 6.1% (male 1,177,999/female 1,769,038) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 53.9 %youth dependency ratio: 45.4 %elderly dependency ratio: 8.5 %potential support ratio: 11.7 (2013)Median age:total: 25.5 yearsmale: 25.2 yearsfemale: 25.8 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:-0.45% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 222Birth rate:19.14 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 94Death rate:17.36 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 1Net migration rate:-6.24 migrant(s)/1,000 populationcountry comparison to the world: 197note: there is an increasing flow of Zimbabweans into South Africa and Botswana in search of better economic opportunities (2013 est.)Urbanization:urban population: 62% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 1.21% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:Johannesburg 3.607 million; Cape Town 3.353 million; Ekurhuleni (East Rand) 3.144 million; Durban 2.837 million; PRETORIA (capital) 1.404 million (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.02 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.01 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.03 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.07 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.76 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.67 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:22.5 (2003 est.)Maternal mortality rate:300 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 39Infant mortality rate:total: 42.15 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 52male: 45.9 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 38.33 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 49.48 yearscountry comparison to the world: 222male: 50.43 yearsfemale: 48.51 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:2.25 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 100Contraceptive prevalence rate:59.9% (2003/04)Health expenditures:8.9% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 46Physicians density:0.77 physicians/1,000 population (2004)Hospital bed density:2.84 beds/1,000 population (2005)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 99% of populationrural: 79% of populationtotal: 91% of populationunimproved:urban: 1% of populationrural: 21% of populationtotal: 9% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 86% of populationrural: 67% of populationtotal: 79% of populationunimproved:urban: 14% of populationrural: 33% of populationtotal: 21% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:17.8% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 4HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:5.6 million (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 1HIV/AIDS - deaths:310,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 1Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: intermediatefood or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid feverwater contact disease: schistosomiasis (2013)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:31.3% (2008)country comparison to the world: 24Children under the age of 5 years underweight:11.6% (2005)country comparison to the world: 63Education expenditures:6% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 38Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 93%male: 93.9%female: 92.2% (2011 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 13 yearsmale: 13 yearsfemale: 13 years (2004)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 49.8%country comparison to the world: 5male: 45.4%female: 55% (2011)Government ::South AfricaCountry name:conventional long form: Republic of South Africaconventional short form: South Africaformer: Union of South Africaabbreviation: RSAGovernment type:republicCapital:name: Pretoria (administrative capital)geographic coordinates: 25 42 S, 28 13 Etime difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)note: Cape Town (legislative capital); Bloemfontein (judicial capital)Administrative divisions:9 provinces; Eastern Cape, Free State, Gauteng, KwaZulu-Natal, Limpopo, Mpumalanga, Northern Cape, North-West, Western CapeIndependence:31 May 1910 (Union of South Africa formed from four British colonies: Cape Colony, Natal, Transvaal, and Orange Free State); 31 May 1961 (republic declared); 27 April 1994 (majority rule)National holiday:Freedom Day, 27 April (1994)Constitution:10 December 1996; note - certified by the Constitutional Court 4 December 1996; was signed by then President MANDELA 10 December 1996; and entered into effect 4 February 1997Legal system:mixed legal system of Roman-Dutch civil law, English common law, and customary lawInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdictionSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President Jacob ZUMA (since 9 May 2009); Deputy President Kgalema MOTLANTHE (since 11 May 2009); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of governmenthead of government: President Jacob ZUMA (since 9 May 2009); Deputy President Kgalema MOTLANTHE (since 11 May 2009)cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: president elected by the National Assembly for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 6 May 2009 (next to be held in 2014)election results: Jacob ZUMA elected president; National Assembly vote - Jacob ZUMA 277, Mvume DANDALA 47, other 76Legislative branch:bicameral Parliament consisting of the National Council of Provinces (90 seats; 10 members elected by each of the nine provincial legislatures for five-year terms; has special powers to protect regional interests, including the safeguarding of cultural and linguistic traditions among ethnic minorities) and the National Assembly (400 seats; members elected by popular vote under a system of proportional representation to serve five-year terms)elections: National Assembly and National Council of Provinces - last held on 22 April 2009 (next to be held in April 2014)election results: National Council of Provinces - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA; National Assembly - percent of vote by party - ANC 65.9%, DA 16.7%, COPE 7.4%, IFP 4.6%, other 5.4%; seats by party - ANC 264, DA 67, COPE 30, IFP 18, other 21Judicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court of Appeals (consists of the court president, deputy president, and 21 judges); Constitutional Court (consists of the chief and deputy chief justices and 9 judges)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court of Appeals president and vice-president appointed by the national president after consultation with the Joint Services Commission (JSC), a 22-member body of judicial and other government officials, and a law academics; other Supreme Court judges appointed by the national president on the advice of the JSC and hold office until discharged from active service in terms of an Act of Parliament; Constitutional Court chief and deputy chief justices appointed by the national president after consultation with the JSC and with heads of the National Assembly; other Constitutional Court judges appointed by the national president after consultation with the chief justice and leaders of the National Assembly; Constitutional Court judges appointed for 12-year non-renewable terms or until age 70subordinate courts: High Courts; Magistrates' Courts; labor courts; land claims courts;Political parties and leaders:African Christian Democratic Party or ACDP [Kenneth MESHOE]African National Congress or ANC [Jacob ZUMA]Congress of the People or COPE [Mosiuoa LEKOTA]Democratic Alliance or DA [Helen ZILLE]Freedom Front Plus or FF+ [Pieter MULDER]Inkatha Freedom Party or IFP [Mangosuthu BUTHELEZI]Pan-Africanist Congress or PAC [Motsoko PHEKO]United Christian Democratic Party or UCDP [Lucas MANGOPE]United Democratic Movement or UDM [Bantu HOLOMISA]Political pressure groups and leaders:Congress of South African Trade Unions or COSATU [Zwelinzima VAVI, general secretary]South African Communist Party or SACP [Blade NZIMANDE, general secretary]South African National Civics Organization or SANCO [Mlungisi HLONGWANE, national president]note: COSATU and SACP are in a formal alliance with the ANCInternational organization participation:ACP, AfDB, AU, BIS, BRICS, C, CD, FAO, FATF, G-20, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MONUSCO, NAM, NSG, OECD (Enhanced Engagement, OPCW, Paris Club (associate), PCA, SACU, SADC, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNITAR, UNSC (temporary), UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZCDiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Ebrahim RASOOLchancery: 3051 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 232-4400FAX: [1] (202) 265-1607consulate(s) general: Chicago, Los Angeles, New YorkDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Donald H. GIPSembassy: 877 Pretorius Street, Pretoriamailing address: P. O. Box 9536, Pretoria 0001telephone: [27] (12) 431-4000FAX: [27] (12) 342-2299consulate(s) general: Cape Town, Durban, JohannesburgFlag description:two equal width horizontal bands of red (top) and blue separated by a central green band that splits into a horizontal Y, the arms of which end at the corners of the hoist side; the Y embraces a black isosceles triangle from which the arms are separated by narrow yellow bands; the red and blue bands are separated from the green band and its arms by narrow white stripes; the flag colors do not have any official symbolism, but the Y stands for the ""convergence of diverse elements within South African society, taking the road ahead in unity""; black, yellow, and green are found on the flag of the African National Congress, while red, white, and blue are the colors in the flags of the Netherlands and the UK, whose settlers ruled South Africa during the colonial eranote: the South African flag is one of only two national flags to display six colors as part of its primary design, the other is South Sudan'sNational symbol(s):springbok antelopeNational anthem:name: ""National Anthem of South Africa""lyrics/music: Enoch SONTONGA and Cornelius Jacob LANGENHOVEN/Enoch SONTONGA and Marthinus LOURENS de Villiersnote: adopted 1994; the anthem is a combination of ""N'kosi Sikelel' iAfrica"" (God Bless Africa) and ""Die Stem van Suid Afrika"" (The Call of South Africa), which were respectively the anthems of the non-white and white communities under apartheid; the official lyrics contain a mixture of Xhosa, Zulu, Sesotho, Afrikaans, and English; the music incorporates the melody used in the Tanzanian and Zambian anthemsEconomy ::South AfricaEconomy - overview:South Africa is a middle-income, emerging market with an abundant supply of natural resources; well-developed financial, legal, communications, energy, and transport sectors and a stock exchange that is the 15th largest in the world. Even though the country possesses modern infrastructure that support a relatively efficient distribution of goods to major urban centers throughout the region, some components retard growth. The economy began to slow in the second half of 2007 due to an electricity crisis. State power supplier Eskom encountered problems with aging plants and meeting electricity demand necessitating ""load-shedding"" cuts in 2007 and 2008 to residents and businesses in the major cities. Subsequently, the global financial crisis reduced commodity prices and world demand. GDP fell nearly 2% in 2009 but has recovered since then. Unemployment, poverty, and inequality remain a challenge, with official unemployment at nearly 25% of the work force. Eskom has built two new power stations and installed new power demand management programs to improve power grid reliability. South Africa's economic policy has focused on controlling inflation, however, the country has had significant budget deficits that restrict its ability to deal with pressing economic problems. The current government faces growing pressure from special interest groups to use state-owned enterprises to deliver basic services to low-income areas and to increase job growth.GDP (purchasing power parity):$592 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 26$577.3 billion (2011 est.)$558 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$384.3 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:2.5% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1253.5% (2011 est.)3.1% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$11,600 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 109$11,400 (2011 est.)$11,200 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:13.1% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 11316.1% of GDP (2011 est.)16.4% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 60.4%government consumption: 22.4%investment in fixed capital: 19.2%investment in inventories: 1%exports of goods and services: 28.3%imports of goods and services: -31.3%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 2.6%industry: 29.3%services: 68.1% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:corn, wheat, sugarcane, fruits, vegetables; beef, poultry, mutton, wool, dairy productsIndustries:mining (world's largest producer of platinum, gold, chromium), automobile assembly, metalworking, machinery, textiles, iron and steel, chemicals, fertilizer, foodstuffs, commercial ship repairIndustrial production growth rate:0.8% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 123Labor force:18.06 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 34Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 9%industry: 26%services: 65% (2007 est.)Unemployment rate:22.7% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 16924.9% (2011 est.)Population below poverty line:31.3% (2009 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 1.2%highest 10%: 51.7% (2009 est.)Distribution of family income - Gini index:63.1 (2005)country comparison to the world: 259.3 (1994)Budget:revenues: $99.56 billionexpenditures: $117.8 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:25.9% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 120Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-4.7% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 162Public debt:40% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 8739.2% of GDP (2011 est.)Fiscal year:1 April - 31 MarchInflation rate (consumer prices):5.7% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1595% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:5% (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 387% (31 December 2009)Commercial bank prime lending rate:8.75% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1029% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$122 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 31$117.3 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$277 billion (31 December 2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 34$314.1 billion (31 December 2010 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$298.8 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 35$284.7 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$1.038 trillion (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 16$855.7 billion (31 December 2011)$1.013 trillion (31 December 2010)Current account balance:-$21.33 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 183-$13.68 billion (2011 est.)Exports:$100.7 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 39$102.9 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:gold, diamonds, platinum, other metals and minerals, machinery and equipmentExports - partners:China 14.5%, US 7.9%, Japan 5.7%, Germany 5.5%, India 4.5%, UK 4.1% (2012)Imports:$105 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 34$100.4 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:machinery and equipment, chemicals, petroleum products, scientific instruments, foodstuffsImports - partners:China 14.9%, Germany 10.1%, US 7.3%, Saudi Arabia 7.2%, India 4.6%, Japan 4.5% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$50.7 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 37$48.87 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$137.5 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 37$113.1 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$139.7 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 31$134.4 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$78.25 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 30$78.53 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Exchange rates:rand (ZAR) per US dollar -8.2031 (2012 est.)7.2597 (2011 est.)7.3212 (2010 est.)8.42 (2009)7.9576 (2008)Energy ::South AfricaElectricity - production:257.9 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 15Electricity - consumption:234.2 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 16Electricity - exports:15.04 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 11Electricity - imports:10.06 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 22Electricity - installed generating capacity:44.26 million kW (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 21Electricity - from fossil fuels:90.8% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 75Electricity - from nuclear fuels:4.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 24Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:1.5% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 140Electricity - from other renewable sources:0.5% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 75Crude oil - production:169,000 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 40Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 178Crude oil - imports:402,300 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 21Crude oil - proved reserves:15 million bbl (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 87Refined petroleum products - production:516,100 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 31Refined petroleum products - consumption:590,900 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 29Refined petroleum products - exports:49,430 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 59Refined petroleum products - imports:60,290 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Natural gas - production:970 million cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 64Natural gas - consumption:4.01 billion cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 66Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 174Natural gas - imports:3.04 billion cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 42Natural gas - proved reserves:27.16 million cu m (1 January 2006 est.)country comparison to the world: 103Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:465.1 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 12Communications ::South AfricaTelephones - main lines in use:4.127 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 42Telephones - mobile cellular:64 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 20Telephone system:general assessment: the system is the best developed and most modern in Africadomestic: combined fixed-line and mobile-cellular teledensity is roughly 140 telephones per 100 persons; consists of carrier-equipped open-wire lines, coaxial cables, microwave radio relay links, fiber-optic cable, radiotelephone communication stations, and wireless local loops; key centers are Bloemfontein, Cape Town, Durban, Johannesburg, Port Elizabeth, and Pretoriainternational: country code - 27; the SAT-3/WASC and SAFE fiber-optic submarine cable systems connect South Africa to Europe and Asia; the EASSy fiber-optic cable system connects with Europe and North America; satellite earth stations - 3 Intelsat (1 Indian Ocean and 2 Atlantic Ocean) (2011)Broadcast media:the South African Broadcasting Corporation (SABC) operates 4 TV stations, 3 are free-to-air and 1 is pay TV; e.tv, a private station, is accessible to more than half the population; multiple subscription TV services provide a mix of local and international channels; well developed mix of public and private radio stations at the national, regional, and local levels; the SABC radio network, state-owned and controlled but nominally independent, operates 18 stations, one for each of the 11 official languages, 4 community stations, and 3 commercial stations; more than 100 community-based stations extend coverage to rural areas (2007)Internet country code:.zaInternet hosts:4.761 million (2012)country comparison to the world: 23Internet users:4.42 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 54Transportation ::South AfricaAirports:566 (2013)country comparison to the world: 11Airports - with paved runways:total: 144over 3,047 m: 112,438 to 3,047 m: 71,524 to 2,437 m: 52914 to 1,523 m: 65under 914 m: 9 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 4222,438 to 3,047 m: 11,524 to 2,437 m: 31914 to 1,523 m: 258under 914 m:132 (2013)Heliports:1 (2013)Pipelines:condensate 94 km; gas 1,293 km; oil 992 km; refined products 1,460 km (2013)Railways:total: 20,192 kmcountry comparison to the world: 14narrow gauge: 19,756 km 1.065-m gauge (8,271 km electrified); 122 km 0.750-m gauge; 314 km 0.610-m gauge (2008)Roadways:total: 362,099 kmcountry comparison to the world: 18paved: 73,506 km (includes 239 km of expressways)unpaved: 288,593 km (2002)Merchant marine:total: 3country comparison to the world: 134by type: petroleum tanker 3registered in other countries: 19 (Australia 1, Isle of Man 2, Mexico 1, NZ 1, Seychelles 1, Singapore 13) (2010)Ports and terminals:Cape Town, Durban, Port Elizabeth, Richards Bay, Saldanha BayMilitary ::South AfricaMilitary branches:South African National Defense Force (SANDF): South African Army, South African Navy (SAN), South African Air Force (SAAF), South African Military Health Services (2013)Military service age and obligation:18 years of age for voluntary military service; women are eligible to serve in noncombat roles; 2-year service obligation (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 13,439,781females age 16-49: 12,473,641 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 7,617,063females age 16-49: 6,476,264 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 482,122female: 485,017 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:1.7% of GDP (2006)country comparison to the world: 85Military - note:with the end of apartheid and the establishment of majority rule, former military, black homelands forces, and ex-opposition forces were integrated into the South African National Defense Force (SANDF); as of 2003 the integration process was considered completeTransnational Issues ::South AfricaDisputes - international:South Africa has placed military units to assist police operations along the border of Lesotho, Zimbabwe, and Mozambique to control smuggling, poaching, and illegal migration; the governments of South Africa and Namibia have not signed or ratified the text of the 1994 Surveyor's General agreement placing the boundary in the middle of the Orange RiverRefugees and internally displaced persons:refugees (country of origin): 17,864 (Somalia); 13,386 (Democratic Republic of Congo); 5,805 (Angola); 5,538 (Ethiopia) (2012)Illicit drugs:transshipment center for heroin, hashish, and cocaine, as well as a major cultivator of marijuana in its own right; cocaine and heroin consumption on the rise; world's largest market for illicit methaqualone, usually imported illegally from India through various east African countries, but increasingly producing its own synthetic drugs for domestic consumption; attractive venue for money launderers given the increasing level of organized criminal and narcotics activity in the region and the size of the South African economy"
Introduction ::South AfricaBackground:Dutch traders landed at the southern tip of modern day South Africa in 1652 and established a stopover point on the spice route between the Netherlands and the Far East, founding the city of Cape Town. After the British seized the Cape of Good Hope area in 1806, many of the Dutch settlers (the Boers) trekked north to found their own republics. The discovery of diamonds (1867) and gold (1886) spurred wealth and immigration and intensified the subjugation of the native inhabitants. The Boers resisted British encroachments but were defeated in the Boer War (1899-1902); however, the British and the Afrikaners, as the Boers became known, ruled together beginning in 1910 under the Union of South Africa, which became a republic in 1961 after a whites-only referendum. In 1948, the National Party was voted into power and instituted a policy of apartheid - the separate development of the races - which favored the white minority at the expense of the black majority. The African National Congress (ANC) led the opposition to apartheid and many top ANC leaders, such as Nelson MANDELA, spent decades in South Africa's prisons. Internal protests and insurgency, as well as boycotts by some Western nations and institutions, led to the regime's eventual willingness to negotiate a peaceful transition to majority rule. The first multi-racial elections in 1994 brought an end to apartheid and ushered in majority rule under an ANC-led government. South Africa since then has struggled to address apartheid-era imbalances in decent housing, education, and health care. ANC infighting, which has grown in recent years, came to a head in September 2008 when President Thabo MBEKI resigned, and Kgalema MOTLANTHE, the party's General-Secretary, succeeded him as interim president. Jacob ZUMA became president after the ANC won general elections in April 2009.Geography ::South AfricaLocation:Southern Africa, at the southern tip of the continent of AfricaGeographic coordinates:29 00 S, 24 00 EArea:total: 1,219,090 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 25land: 1,214,470 sq kmwater: 4,620 sq kmnote: includes Prince Edward Islands (Marion Island and Prince Edward Island)Area - comparative:slightly less than twice the size of TexasLand boundaries:total: 4,862 kmborder countries: Botswana 1,840 km, Lesotho 909 km, Mozambique 491 km, Namibia 967 km, Swaziland 430 km, Zimbabwe 225 kmCoastline:2,798 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontinental shelf: 200 nm or to edge of the continental marginClimate:mostly semiarid; subtropical along east coast; sunny days, cool nightsTerrain:vast interior plateau rimmed by rugged hills and narrow coastal plainElevation extremes:lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 mhighest point: Njesuthi 3,408 mNatural resources:gold, chromium, antimony, coal, iron ore, manganese, nickel, phosphates, tin, rare earth elements, uranium, gem diamonds, platinum, copper, vanadium, salt, natural gasLand use:arable land: 9.87%permanent crops: 0.34%other: 89.79% (2011)Irrigated land:16,700 sq km (2012)Total renewable water resources:51.4 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 12.5 cu km/yr (36%/7%/57%)per capita: 271.7 cu m/yr (2005)Natural hazards:prolonged droughtsvolcanism: the volcano forming Marion Island in the Prince Edward Islands, which last erupted in 2004, is South Africa's only active volcanoEnvironment - current issues:lack of important arterial rivers or lakes requires extensive water conservation and control measures; growth in water usage outpacing supply; pollution of rivers from agricultural runoff and urban discharge; air pollution resulting in acid rain; soil erosion; desertificationEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:South Africa completely surrounds Lesotho and almost completely surrounds SwazilandPeople and Society ::South AfricaNationality:noun: South African(s)adjective: South AfricanEthnic groups:black African 79%, white 9.6%, colored 8.9%, Indian/Asian 2.5% (2001 census)Languages:IsiZulu (official) 23.82%, IsiXhosa (official) 17.64%, Afrikaans (official) 13.35%, Sepedi (offcial) 9.39%, English (official) 8.2%, Setswana (official) 8.2%, Sesotho (official) 7.93%, Xitsonga (official) 4.44%, siSwati (official) 2.66%, Tshivenda (official) 2.28%, isiNdebele (official) 1.59%, other 0.5% (2001 census)Religions:Protestant 36.6% (Zionist Christian 11.1%, Pentecostal/Charismatic 8.2%, Methodist 6.8%, Dutch Reformed 6.7%, Anglican 3.8%), Catholic 7.1%, Muslim 1.5%, other Christian 36%, other 2.3%, unspecified 1.4%, none 15.1% (2001 census)Population:48,601,098 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 26note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expectedAge structure:0-14 years: 28.3% (male 6,909,066/female 6,866,163)15-24 years: 20.6% (male 5,041,412/female 4,960,190)25-54 years: 38.1% (male 9,561,452/female 8,948,398)55-64 years: 6.9% (male 1,450,420/female 1,916,960)65 years and over: 6.1% (male 1,177,999/female 1,769,038) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 53.9 %youth dependency ratio: 45.4 %elderly dependency ratio: 8.5 %potential support ratio: 11.7 (2013)Median age:total: 25.5 yearsmale: 25.2 yearsfemale: 25.8 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:-0.45% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 222Birth rate:19.14 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 94Death rate:17.36 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 1Net migration rate:-6.24 migrant(s)/1,000 populationcountry comparison to the world: 197note: there is an increasing flow of Zimbabweans into South Africa and Botswana in search of better economic opportunities (2013 est.)Urbanization:urban population: 62% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 1.21% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:Johannesburg 3.607 million; Cape Town 3.353 million; Ekurhuleni (East Rand) 3.144 million; Durban 2.837 million; PRETORIA (capital) 1.404 million (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.02 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.01 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.03 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.07 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.76 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.67 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:22.5 (2003 est.)Maternal mortality rate:300 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 39Infant mortality rate:total: 42.15 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 52male: 45.9 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 38.33 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 49.48 yearscountry comparison to the world: 222male: 50.43 yearsfemale: 48.51 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:2.25 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 100Contraceptive prevalence rate:59.9% (2003/04)Health expenditures:8.9% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 46Physicians density:0.77 physicians/1,000 population (2004)Hospital bed density:2.84 beds/1,000 population (2005)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 99% of populationrural: 79% of populationtotal: 91% of populationunimproved:urban: 1% of populationrural: 21% of populationtotal: 9% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 86% of populationrural: 67% of populationtotal: 79% of populationunimproved:urban: 14% of populationrural: 33% of populationtotal: 21% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:17.8% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 4HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:5.6 million (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 1HIV/AIDS - deaths:310,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 1Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: intermediatefood or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid feverwater contact disease: schistosomiasis (2013)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:31.3% (2008)country comparison to the world: 24Children under the age of 5 years underweight:11.6% (2005)country comparison to the world: 63Education expenditures:6% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 38Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 93%male: 93.9%female: 92.2% (2011 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 13 yearsmale: 13 yearsfemale: 13 years (2004)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 49.8%country comparison to the world: 5male: 45.4%female: 55% (2011)Government ::South AfricaCountry name:conventional long form: Republic of South Africaconventional short form: South Africaformer: Union of South Africaabbreviation: RSAGovernment type:republicCapital:name: Pretoria (administrative capital)geographic coordinates: 25 42 S, 28 13 Etime difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)note: Cape Town (legislative capital); Bloemfontein (judicial capital)Administrative divisions:9 provinces; Eastern Cape, Free State, Gauteng, KwaZulu-Natal, Limpopo, Mpumalanga, Northern Cape, North-West, Western CapeIndependence:31 May 1910 (Union of South Africa formed from four British colonies: Cape Colony, Natal, Transvaal, and Orange Free State); 31 May 1961 (republic declared); 27 April 1994 (majority rule)National holiday:Freedom Day, 27 April (1994)Constitution:10 December 1996; note - certified by the Constitutional Court 4 December 1996; was signed by then President MANDELA 10 December 1996; and entered into effect 4 February 1997Legal system:mixed legal system of Roman-Dutch civil law, English common law, and customary lawInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdictionSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President Jacob ZUMA (since 9 May 2009); Deputy President Kgalema MOTLANTHE (since 11 May 2009); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of governmenthead of government: President Jacob ZUMA (since 9 May 2009); Deputy President Kgalema MOTLANTHE (since 11 May 2009)cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: president elected by the National Assembly for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 6 May 2009 (next to be held in 2014)election results: Jacob ZUMA elected president; National Assembly vote - Jacob ZUMA 277, Mvume DANDALA 47, other 76Legislative branch:bicameral Parliament consisting of the National Council of Provinces (90 seats; 10 members elected by each of the nine provincial legislatures for five-year terms; has special powers to protect regional interests, including the safeguarding of cultural and linguistic traditions among ethnic minorities) and the National Assembly (400 seats; members elected by popular vote under a system of proportional representation to serve five-year terms)elections: National Assembly and National Council of Provinces - last held on 22 April 2009 (next to be held in April 2014)election results: National Council of Provinces - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA; National Assembly - percent of vote by party - ANC 65.9%, DA 16.7%, COPE 7.4%, IFP 4.6%, other 5.4%; seats by party - ANC 264, DA 67, COPE 30, IFP 18, other 21Judicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court of Appeals (consists of the court president, deputy president, and 21 judges); Constitutional Court (consists of the chief and deputy chief justices and 9 judges)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court of Appeals president and vice-president appointed by the national president after consultation with the Joint Services Commission (JSC), a 22-member body of judicial and other government officials, and a law academics; other Supreme Court judges appointed by the national president on the advice of the JSC and hold office until discharged from active service in terms of an Act of Parliament; Constitutional Court chief and deputy chief justices appointed by the national president after consultation with the JSC and with heads of the National Assembly; other Constitutional Court judges appointed by the national president after consultation with the chief justice and leaders of the National Assembly; Constitutional Court judges appointed for 12-year non-renewable terms or until age 70subordinate courts: High Courts; Magistrates' Courts; labor courts; land claims courts;Political parties and leaders:African Christian Democratic Party or ACDP [Kenneth MESHOE]African National Congress or ANC [Jacob ZUMA]Congress of the People or COPE [Mosiuoa LEKOTA]Democratic Alliance or DA [Helen ZILLE]Freedom Front Plus or FF+ [Pieter MULDER]Inkatha Freedom Party or IFP [Mangosuthu BUTHELEZI]Pan-Africanist Congress or PAC [Motsoko PHEKO]United Christian Democratic Party or UCDP [Lucas MANGOPE]United Democratic Movement or UDM [Bantu HOLOMISA]Political pressure groups and leaders:Congress of South African Trade Unions or COSATU [Zwelinzima VAVI, general secretary]South African Communist Party or SACP [Blade NZIMANDE, general secretary]South African National Civics Organization or SANCO [Mlungisi HLONGWANE, national president]note: COSATU and SACP are in a formal alliance with the ANCInternational organization participation:ACP, AfDB, AU, BIS, BRICS, C, CD, FAO, FATF, G-20, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MONUSCO, NAM, NSG, OECD (Enhanced Engagement, OPCW, Paris Club (associate), PCA, SACU, SADC, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNITAR, UNSC (temporary), UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZCDiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Ebrahim RASOOLchancery: 3051 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 232-4400FAX: [1] (202) 265-1607consulate(s) general: Chicago, Los Angeles, New YorkDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Donald H. GIPSembassy: 877 Pretorius Street, Pretoriamailing address: P. O. Box 9536, Pretoria 0001telephone: [27] (12) 431-4000FAX: [27] (12) 342-2299consulate(s) general: Cape Town, Durban, JohannesburgFlag description:two equal width horizontal bands of red (top) and blue separated by a central green band that splits into a horizontal Y, the arms of which end at the corners of the hoist side; the Y embraces a black isosceles triangle from which the arms are separated by narrow yellow bands; the red and blue bands are separated from the green band and its arms by narrow white stripes; the flag colors do not have any official symbolism, but the Y stands for the ""convergence of diverse elements within South African society, taking the road ahead in unity""; black, yellow, and green are found on the flag of the African National Congress, while red, white, and blue are the colors in the flags of the Netherlands and the UK, whose settlers ruled South Africa during the colonial eranote: the South African flag is one of only two national flags to display six colors as part of its primary design, the other is South Sudan'sNational symbol(s):springbok antelopeNational anthem:name: ""National Anthem of South Africa""lyrics/music: Enoch SONTONGA and Cornelius Jacob LANGENHOVEN/Enoch SONTONGA and Marthinus LOURENS de Villiersnote: adopted 1994; the anthem is a combination of ""N'kosi Sikelel' iAfrica"" (God Bless Africa) and ""Die Stem van Suid Afrika"" (The Call of South Africa), which were respectively the anthems of the non-white and white communities under apartheid; the official lyrics contain a mixture of Xhosa, Zulu, Sesotho, Afrikaans, and English; the music incorporates the melody used in the Tanzanian and Zambian anthemsEconomy ::South AfricaEconomy - overview:South Africa is a middle-income, emerging market with an abundant supply of natural resources; well-developed financial, legal, communications, energy, and transport sectors and a stock exchange that is the 15th largest in the world. Even though the country possesses modern infrastructure that support a relatively efficient distribution of goods to major urban centers throughout the region, some components retard growth. The economy began to slow in the second half of 2007 due to an electricity crisis. State power supplier Eskom encountered problems with aging plants and meeting electricity demand necessitating ""load-shedding"" cuts in 2007 and 2008 to residents and businesses in the major cities. Subsequently, the global financial crisis reduced commodity prices and world demand. GDP fell nearly 2% in 2009 but has recovered since then. Unemployment, poverty, and inequality remain a challenge, with official unemployment at nearly 25% of the work force. Eskom has built two new power stations and installed new power demand management programs to improve power grid reliability. South Africa's economic policy has focused on controlling inflation, however, the country has had significant budget deficits that restrict its ability to deal with pressing economic problems. The current government faces growing pressure from special interest groups to use state-owned enterprises to deliver basic services to low-income areas and to increase job growth.GDP (purchasing power parity):$592 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 26$577.3 billion (2011 est.)$558 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$384.3 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:2.5% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1253.5% (2011 est.)3.1% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$11,600 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 109$11,400 (2011 est.)$11,200 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:13.1% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 11316.1% of GDP (2011 est.)16.4% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 60.4%government consumption: 22.4%investment in fixed capital: 19.2%investment in inventories: 1%exports of goods and services: 28.3%imports of goods and services: -31.3%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 2.6%industry: 29.3%services: 68.1% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:corn, wheat, sugarcane, fruits, vegetables; beef, poultry, mutton, wool, dairy productsIndustries:mining (world's largest producer of platinum, gold, chromium), automobile assembly, metalworking, machinery, textiles, iron and steel, chemicals, fertilizer, foodstuffs, commercial ship repairIndustrial production growth rate:0.8% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 123Labor force:18.06 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 34Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 9%industry: 26%services: 65% (2007 est.)Unemployment rate:22.7% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 16924.9% (2011 est.)Population below poverty line:31.3% (2009 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 1.2%highest 10%: 51.7% (2009 est.)Distribution of family income - Gini index:63.1 (2005)country comparison to the world: 259.3 (1994)Budget:revenues: $99.56 billionexpenditures: $117.8 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:25.9% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 120Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-4.7% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 162Public debt:40% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 8739.2% of GDP (2011 est.)Fiscal year:1 April - 31 MarchInflation rate (consumer prices):5.7% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1595% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:5% (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 387% (31 December 2009)Commercial bank prime lending rate:8.75% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1029% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$122 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 31$117.3 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$277 billion (31 December 2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 34$314.1 billion (31 December 2010 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$298.8 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 35$284.7 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$1.038 trillion (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 16$855.7 billion (31 December 2011)$1.013 trillion (31 December 2010)Current account balance:-$21.33 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 183-$13.68 billion (2011 est.)Exports:$100.7 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 39$102.9 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:gold, diamonds, platinum, other metals and minerals, machinery and equipmentExports - partners:China 14.5%, US 7.9%, Japan 5.7%, Germany 5.5%, India 4.5%, UK 4.1% (2012)Imports:$105 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 34$100.4 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:machinery and equipment, chemicals, petroleum products, scientific instruments, foodstuffsImports - partners:China 14.9%, Germany 10.1%, US 7.3%, Saudi Arabia 7.2%, India 4.6%, Japan 4.5% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$50.7 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 37$48.87 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$137.5 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 37$113.1 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$139.7 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 31$134.4 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$78.25 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 30$78.53 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Exchange rates:rand (ZAR) per US dollar -8.2031 (2012 est.)7.2597 (2011 est.)7.3212 (2010 est.)8.42 (2009)7.9576 (2008)Energy ::South AfricaElectricity - production:257.9 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 15Electricity - consumption:234.2 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 16Electricity - exports:15.04 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 11Electricity - imports:10.06 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 22Electricity - installed generating capacity:44.26 million kW (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 21Electricity - from fossil fuels:90.8% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 75Electricity - from nuclear fuels:4.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 24Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:1.5% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 140Electricity - from other renewable sources:0.5% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 75Crude oil - production:169,000 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 40Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 178Crude oil - imports:402,300 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 21Crude oil - proved reserves:15 million bbl (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 87Refined petroleum products - production:516,100 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 31Refined petroleum products - consumption:590,900 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 29Refined petroleum products - exports:49,430 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 59Refined petroleum products - imports:60,290 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Natural gas - production:970 million cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 64Natural gas - consumption:4.01 billion cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 66Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 174Natural gas - imports:3.04 billion cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 42Natural gas - proved reserves:27.16 million cu m (1 January 2006 est.)country comparison to the world: 103Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:465.1 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 12Communications ::South AfricaTelephones - main lines in use:4.127 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 42Telephones - mobile cellular:64 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 20Telephone system:general assessment: the system is the best developed and most modern in Africadomestic: combined fixed-line and mobile-cellular teledensity is roughly 140 telephones per 100 persons; consists of carrier-equipped open-wire lines, coaxial cables, microwave radio relay links, fiber-optic cable, radiotelephone communication stations, and wireless local loops; key centers are Bloemfontein, Cape Town, Durban, Johannesburg, Port Elizabeth, and Pretoriainternational: country code - 27; the SAT-3/WASC and SAFE fiber-optic submarine cable systems connect South Africa to Europe and Asia; the EASSy fiber-optic cable system connects with Europe and North America; satellite earth stations - 3 Intelsat (1 Indian Ocean and 2 Atlantic Ocean) (2011)Broadcast media:the South African Broadcasting Corporation (SABC) operates 4 TV stations, 3 are free-to-air and 1 is pay TV; e.tv, a private station, is accessible to more than half the population; multiple subscription TV services provide a mix of local and international channels; well developed mix of public and private radio stations at the national, regional, and local levels; the SABC radio network, state-owned and controlled but nominally independent, operates 18 stations, one for each of the 11 official languages, 4 community stations, and 3 commercial stations; more than 100 community-based stations extend coverage to rural areas (2007)Internet country code:.zaInternet hosts:4.761 million (2012)country comparison to the world: 23Internet users:4.42 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 54Transportation ::South AfricaAirports:566 (2013)country comparison to the world: 11Airports - with paved runways:total: 144over 3,047 m: 112,438 to 3,047 m: 71,524 to 2,437 m: 52914 to 1,523 m: 65under 914 m: 9 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 4222,438 to 3,047 m: 11,524 to 2,437 m: 31914 to 1,523 m: 258under 914 m:132 (2013)Heliports:1 (2013)Pipelines:condensate 94 km; gas 1,293 km; oil 992 km; refined products 1,460 km (2013)Railways:total: 20,192 kmcountry comparison to the world: 14narrow gauge: 19,756 km 1.065-m gauge (8,271 km electrified); 122 km 0.750-m gauge; 314 km 0.610-m gauge (2008)Roadways:total: 362,099 kmcountry comparison to the world: 18paved: 73,506 km (includes 239 km of expressways)unpaved: 288,593 km (2002)Merchant marine:total: 3country comparison to the world: 134by type: petroleum tanker 3registered in other countries: 19 (Australia 1, Isle of Man 2, Mexico 1, NZ 1, Seychelles 1, Singapore 13) (2010)Ports and terminals:Cape Town, Durban, Port Elizabeth, Richards Bay, Saldanha BayMilitary ::South AfricaMilitary branches:South African National Defense Force (SANDF): South African Army, South African Navy (SAN), South African Air Force (SAAF), South African Military Health Services (2013)Military service age and obligation:18 years of age for voluntary military service; women are eligible to serve in noncombat roles; 2-year service obligation (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 13,439,781females age 16-49: 12,473,641 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 7,617,063females age 16-49: 6,476,264 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 482,122female: 485,017 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:1.7% of GDP (2006)country comparison to the world: 85Military - note:with the end of apartheid and the establishment of majority rule, former military, black homelands forces, and ex-opposition forces were integrated into the South African National Defense Force (SANDF); as of 2003 the integration process was considered completeTransnational Issues ::South AfricaDisputes - international:South Africa has placed military units to assist police operations along the border of Lesotho, Zimbabwe, and Mozambique to control smuggling, poaching, and illegal migration; the governments of South Africa and Namibia have not signed or ratified the text of the 1994 Surveyor's General agreement placing the boundary in the middle of the Orange RiverRefugees and internally displaced persons:refugees (country of origin): 17,864 (Somalia); 13,386 (Democratic Republic of Congo); 5,805 (Angola); 5,538 (Ethiopia) (2012)Illicit drugs:transshipment center for heroin, hashish, and cocaine, as well as a major cultivator of marijuana in its own right; cocaine and heroin consumption on the rise; world's largest market for illicit methaqualone, usually imported illegally from India through various east African countries, but increasingly producing its own synthetic drugs for domestic consumption; attractive venue for money launderers given the increasing level of organized criminal and narcotics activity in the region and the size of the South African economy"
The World Factbook. 2014.
